Writing post functions
How does it work?
When writing post functions, you can specify a sequence of the following actions:
Jira REST API calls
Variable definitions (e.g. to pass information from one REST call to another)
Writing to the application log.
Additionally, you can use variables from the post function event payload (e.g. issue id, transition details, changes that occurred during the transition). These can be accessed either directly, e.g. issue.id, or within a string, e.g. "${issue.id}".
1. Jira REST API Calls
You can trigger network calls to most Jira REST API endpoints. To set a REST API call, simply type the http method (GET, POST, PUT, or DELETE), followed by the url of the endpoint, and the body, if needed.
Examples
Write a comment on the transitioned issue:
POST "/rest/api/3/issue/${issue.id}/comment"
{
"body": {
"content": [
{
"content": [
{
"text": "My Comment Text",
"type": "text"
}
],
"type": "paragraph"
}
],
"type": "doc",
"version": 1
}
};Auto completion
You can use the auto-completion feature (ctrl + space) to help with the syntax, or to see which REST API calls are available.
For example, by typing POST, you will see a list of all POST endpoints which are available in your post functions. You can filter these results by typing which resource you would like to address, e.g. for issues:
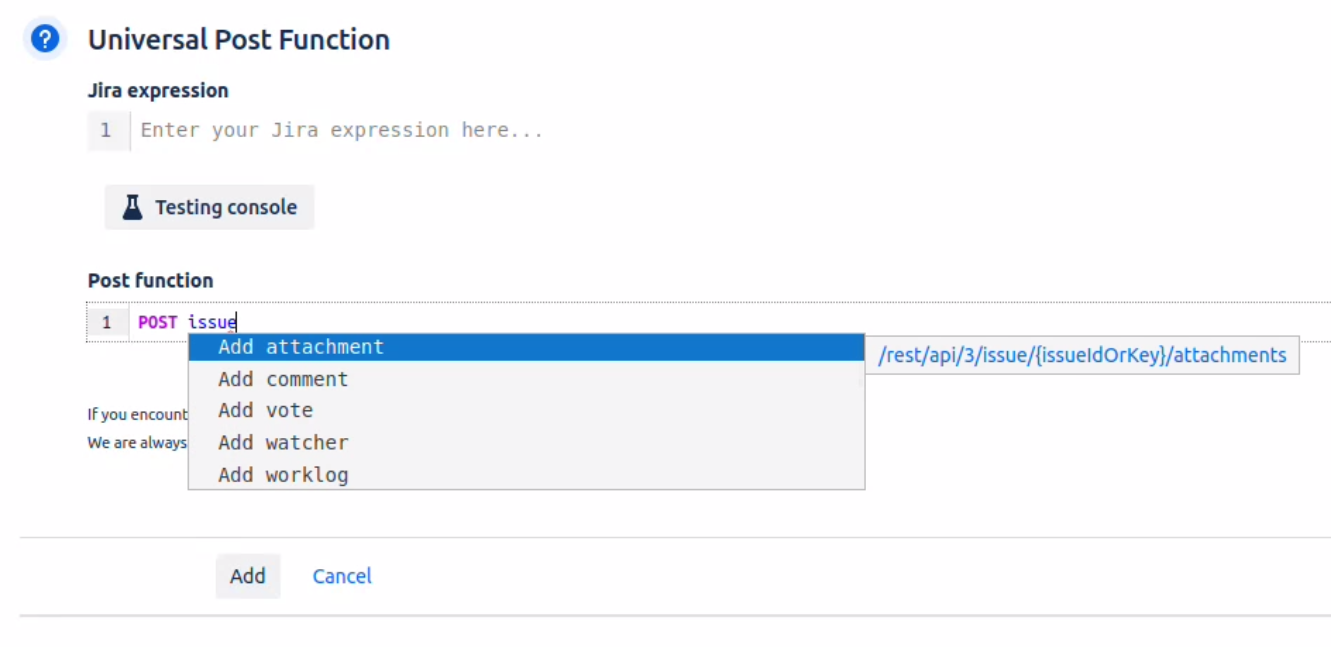
For the selected endpoint, the helper window on the left shows the endpoint uri. Clicking on it will open the respective documentation page in Atlassian’s Jira REST API documentation for further information about the endpoint.
To select an endpoint from the auto completion window, simply click on it, or select it with the arrow keys and press enter.
2. Define Variables
You can define variables for further usage throughout your post function. This is helpful, e.g. to capture the response of a REST call. Variables can be used either directly, e.g. issue.id, or within a string, e.g. "${issue.id}".
Examples
Fetch the value of a custom field of the transitioned issue:
let customfield = GET "/rest/api/3/issue/${issue.id}?fields=customfield_10100";Define a shorthand for some variable in the event payload:
let project_name = issue.fields.project.name;Define a custom object
let myObject = { a: "some text", b: "some other text"};3. Logging
You can write anything during the execution of the post function to the app logs. This can be useful for testing and monitoring.
Examples
Log the value of a custom field of the transitioned issue
let moved_issue = GET "/rest/api/3/issue/${issue.id}?fields=customfield_10100";
log("custom field value: ${moved_issue.fields.customfield_10100.value}");